Lactobacillus Acidophilus: A Gut Health Probiotic
There is a lot of buzz around the health benefits of probiotics and for a good reason. Probiotics are microorganisms that support the growth of healthy bacteria in your gut. A well-functioning gut is essential for overall health.
It helps digest food, absorb nutrients, and fight off infection. One probiotic, in particular, Lactobacillus acidophilus (L. acidophilus), has been shown to provide a number of health benefits. Keep reading and learn more.

1What Is Lactobacillus Acidophilus, And What Are Its Health Benefits?
Lactobacillus acidophilus is a probiotic that is commonly found in yogurts and other fermented foods. It has many health benefits, like the ones listed below.
- Boosting the immune system: Lactobacillus acidophilus produces hydrogen peroxide, which kills harmful bacteria and viruses. This makes it an effective tool for boosting the immune system.
- Treating diarrhea: Lactobacillus acidophilus can help treat diarrhea by helping restore the balance of good and bad bacteria in the gut.
- Reducing lactose intolerance: Lactobacillus acidophilus breaks down lactose, making it easier for people with lactose intolerance to digest dairy products.
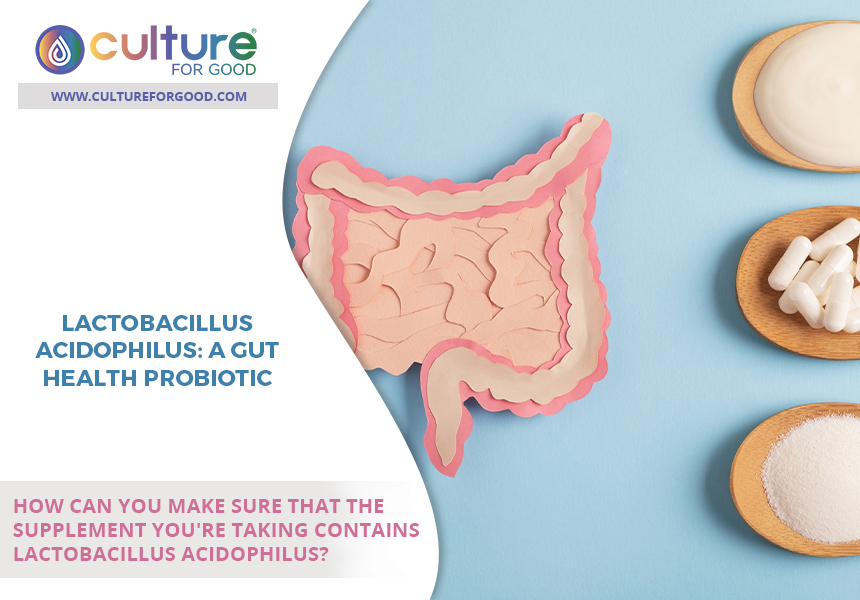
2How Can You Make Sure That The Supplement You’re Taking Contains Lactobacillus Acidophilus?
Make sure that the probiotic supplement you take contains Lactobacillus acidophilus. You can do this by checking the label. If it’s not an ingredient, ask your healthcare professional for a specific probiotic supplement recommendation that does include this probiotic.
It’s crucial to follow their recommended dose. It’s also vital to store the supplement in a cool, dry place. Remember to discard it once it has expired.

3What Are Good Food Sources That Contain Lactobacillus Acidophilus?
Here are some foods that are good sources of Lactobacillus acidophilus.
- Yogurt: Look for yogurts that say “live and active cultures” on the label.
- Kefir: This is a fermented milk drink that contains live probiotic cultures.
- Sauerkraut: This fermented cabbage dish is rich in Lactobacillus acidophilus.
- Pickles: Pickled cucumbers are another great source of this probiotic.
- Tempeh: This fermented soybean product is a great plant-based source of Lactobacillus acidophilus.
There are many ways to incorporate more Lactobacillus acidophilus into your diet. Some suggestions include the following below.
- Eat yogurt or kefir for breakfast or as a snack.
- Use sauerkraut or pickles as condiments on sandwiches or burgers.
- Include tempeh in stir-fries, salads, or wraps.
- Make your fermented foods at home, such as pickles, sauerkraut, or kimchi.

4Are There Any Risks Associated With Taking A Supplement That Contains Lactobacillus Acidophilus?
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that line the gut and support digestion and immune function. Probiotics are considered generally safe. However, some people experience negative side effects when taking them, such as gas, bloating, constipation, and diarrhea.
Additionally, there is some concern that taking probiotics in high doses or for long periods of time could cause harm. Are you considering taking a probiotic supplement that contains Lactobacillus acidophilus? If you are, it is vital to do your research first and speak to your doctor about any potential risks involved.

5How Do You Know If You Are Getting The Most Out Of Your Probiotic Supplement?
It usually takes a few weeks for a person to start seeing results from taking a probiotic supplement. However, it’s essential to remember that everyone is different and that you may not see results until you’ve been taking the supplement for a few months. If you’re not seeing any benefits after taking a probiotic supplement for an extended period, it’s possible that you’re not getting the most out of it.
Look for these signs to help you determine if this is the case.
- You’re not feeling any better after taking the supplement.
- The supplement isn’t making a noticeable impact on your digestive health.
- You’re struggling with recurrent yeast infections or other gut problems.
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it may be time to talk to your doctor about finding a probiotic supplement that works better for you.
Here are some foods and drinks that you may want to avoid while taking a probiotic supplement.
- Alcohol: If you’re taking a probiotic supplement that contains Lactobacillus acidophilus, you should avoid drinking alcohol, as it can kill bacteria.
- Caffeine: Caffeine can also kill the beneficial bacteria in your gut.
- Processed foods: Processed foods are often high in sugar, which can feed the bad bacteria in your gut and lead to problems like yeast overgrowth.
- Dairy products: Dairy products can contain high levels of lactose, which can be difficult for some people to digest.
It’s vital to drink plenty of water while taking a probiotic supplement, as it will help the bacteria colonize your gut. It’s also important to remember that probiotics are living organisms, so they need to be stored properly. Most probiotic supplements should be refrigerated to ensure that the bacteria remain alive and active.
Consuming a probiotic supplement offers many benefits. This is if you’re taking it correctly. Here are five ways to make sure that you’re getting the most out of your probiotic supplement.
- Take the supplement with food. This will help it work better in your gut.
- Don’t exceed the recommended dosage – more is not always better when it comes to probiotics!
- Be consistent in taking the supplement. Don’t skip doses or take it sporadically – this won’t allow good bacteria to colonize your gut and establish themselves, limiting the potential health benefits of consuming probiotics overall.
- Store the bottle in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
- Avoid eating highly processed foods while taking the supplement since these can interfere with how well the bacteria work and reduce its impact.

6Can You Take Too Much Of A Supplement That Contains Lactobacillus Acidophilus?
When it comes to probiotic supplements, it is crucial to be aware of the dosage. Too much of a probiotic supplement that contains Lactobacillus acidophilus can lead to negative side effects. Some of the side effects include gas, bloating, and diarrhea.
It is essential to consult with your doctor before starting any new supplement, including probiotics; your doctor will be able to recommend the dosage that is best for you. There are benefits to taking more than the recommended dosage of a probiotic supplement that contains Lactobacillus acidophilus. Taking a higher dosage can help you get the most out of your probiotic supplement.

7What Should You Do If You Experience Negative Side Effects While Taking A Lactobacillus Acidophilus Supplement?
If you’re experiencing negative side effects while taking a Lactobacillus acidophilus supplement, it’s crucial to consult with your healthcare professional to determine the best course of action. Some potential solutions might include discontinuing the use of the supplement, lowering the dosage, or switching to a different probiotic supplement. However, one of the best ways to determine if the negative side effects are being caused by the Lactobacillus acidophilus supplement is to keep track of when they occur and how severe they are. This can help your healthcare professional make a more accurate diagnosis.
Some potentially negative side effects of taking a Lactobacillus acidophilus supplement might include gas, bloating, diarrhea, or constipation. However, it’s important to keep in mind that these side effects are typically mild and temporary. If you experience any severe or persistent side effects, it’s important to consult with your healthcare professional.
One possible way to minimize the negative side effects of taking a Lactobacillus acidophilus supplement is by taking it with food. This can help reduce stomach upset or nausea. Additionally, you might want to try spacing out your doses throughout the day instead of taking all of them at once. And finally, make sure to drink plenty of fluids while taking a probiotic supplement, as this can also help minimize any adverse effects.
Lactobacillus acidophilus is a probiotic that has been shown to provide a number of health benefits. By taking a supplement that contains L. acidophilus, you can boost your immune system. You also improve your overall health.