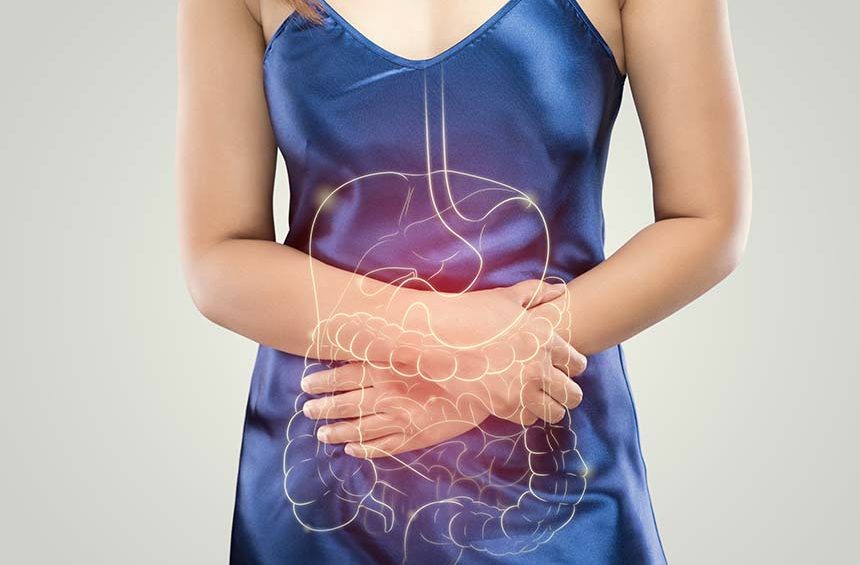
Inflammatory bowel disease is a generalized term for conditions that are characterized by chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. When the immune system functions correctly, it attacks organisms such as bacteria or viruses to protect the body. IBD is the result of a defective immune system responding to environmental triggers that cause inflammation and damage to the intestines. In this article, we will share with you some facts about inflammatory bowel disease.
First, you will learn about Crohn’s disease and ulcerated colitis. Next, we will get more specific and discuss some inflammatory bowel disease information. Then, we will wrap up with complications that can occur with Crohn’s and ulcerated colitis. Once you have finished reading, you will have the information that you need to take the next steps to improve your health.

1Crohn’s Disease And Ulcerated Colitis
Two of the most common and identifiable inflammatory bowel diseases are Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Ulcerative colitis differs from Crohn’s disease in that the inflammation is confined to the upper layers of the intestinal lining, whereas Crohn’s disease causes inflammation throughout the whole thickness of the intestinal wall. The symptoms and treatments are similar for both diseases.
The symptoms common to both Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis include diarrhea, fever and fatigue, abdominal pain and cramps, blood and mucus in the stool, decreased appetite, weight loss, nausea, and impaired growth in children. During periods of flare-ups for both diseases, there is an increased risk of developing inflammation of the eyes, skin lesions, and other disorders, including arthritis. IBD also increases the risk of blood clots. The side effects of some medications prescribed for inflammatory bowel disease may pose a small risk of developing high blood pressure and osteoporosis.

2Inflammatory Bowel Disease Information
Inflammatory bowel disease is not a progressive condition and does not necessarily get worse over time. The severity of symptoms varies from time to time and person to person. Flare-ups of symptoms often seesaw from mild to severe and back to mild again, while others may experience quite long periods of remission, but sometimes, months or even years elapse between flare-ups. IBD interferes with the body’s normal functions. When the disease is medicated to control inflammation, most people can perform normally, but if left untreated, it can be debilitating and sometimes lead to serious complications.
The treatment goal of IBD is to control inflammation, relieve symptoms, and correct nutritional deficiencies. IBD can be diagnosed at any age. Most people who develop inflammatory bowel disease do so before the age of 30, although some don’t contract the disease until their 50s or 60s. Studies have shown that the risk of developing the condition is higher for people who have a close relative, such as a parent, sibling, or child, with IBD. Some non-steroid inflammatory medications that may increase the risk of contracting inflammatory bowel disease are ibuprofen, naproxen sodium, and diclofenac sodium.

3Complications Of Both Diseases
Crohn’s disease can cause parts of the bowel wall to thicken and narrow over time, and when this occurs, the flow of digestive content is blocked. In some cases, surgery is required to remove the diseased section of the bowel. Because Crohn’s disease causes a vitamin B12 deficiency, it is common for patients with the disease to develop anemia. The effects on the body, like diarrhea, abdomen pain, and cramps, make it difficult to eat; malnutrition can occur when the intestine is unable to absorb enough nutrients to provide adequate nourishment. Chronic inflammation often leads to ulcers anywhere in the digestive tract, including the mouth, the anus, and also the genital area.
A complication of ulcerative colitis disease is the enlargement and dilation of the colon. This is associated with severe and intractable constipation and is a serious disorder that’s known as toxic megacolon. Dehydration can also become a problem for people with this disease because of the sometimes excessive diarrhea caused by the disorder.
IBD is a generalized term for conditions that are characterized by chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. The immune system attacks organisms, such as bacteria or viruses, to protect the body when it is functioning correctly. A defective immune system responding to environmental triggers that cause inflammation and damage to the intestines is the result of IBD. In this article, we shared with you some facts about inflammatory bowel disease.
First, you learned about Crohn’s disease and ulcerated colitis. Next, we got more specific and discussed some inflammatory bowel disease information. Then, we wrapped up with complications that can occur with Crohn’s and ulcerated colitis. Now that you have finished reading, you have the information that you need to take the next steps to improve your health.